A
Aggregate – Crushed stone, crushed slag or water worn gravel used for surfacing a built-up roof.
Alligatoring – The cracking of the surfacing bitumen on a built-up roof, producing a pattern of cracks similar to an alligator’s hide; the cracks may or may not extend through the surfacing bitumen. Alligatoring is not always indicative of roof failure or leakage.
Algae Discoloration – A type of roof discoloration caused by algae. Commonly called fungus growth. Many manufactures produce algae resistant shingles. Look for “AR”.
Aluminum paint – An oil based coating mixed with aluminum particles, used for protecting asphalt roofs from UV rays & preserving a roofs life.
Asphalt – A black bitumen material used in roofing in hot or cold form, also called tar.
Asphalt Felt – An asphalt-saturated felt or an asphalt coated felt, primarily used as the base layer on sloped roofs. A form of under lament and can come in #15 & #30. #30 being the thicker of the two.
Asphalt Plastic Cement – An asphalt-based cement used to bond roofing materials. Also known as flashing cement or mastic.
B
Base Flashing – That portion of flashing attached to or resting on the deck to direct the flow of water onto the roof covering.
Built-up Roof– A flat or low pitched roof consisting multiple layers of asphalt and ply sheets.
Bundle(s) – A package of shingles. There a generally 3 bundles to a square but can be 4 or 5 depending on weight. Ex. GAF/ELK 50 year is 5 Bundles per square.
D
Deck – The surface, installed over the supporting framing members, to which the roof is applied.
Dormer – A framed window unit projecting through the sloping plane of a roof.
Downspout – A pipe for draining water from the roof gutters.
Drip Edge – A non-corrosive, non-staining material used along the eaves and rakes, flush with the fascia, to allow water run-off to drip clear of underlying construction.
Drying-In – The application of roofing felt to the rook deck.
E
Eaves – The horizontal, lower edge of a sloped roof.
Elastomeric – A rubber like synthetic polymer that will stretch when pulled and will return quickly to its original shape when released, primarily used for waterproofing walls and vertical surfaces.
F
Fascia – The wood trim covering the rafters and rafter ends, just beneath the drip edge. Located at the end of the eaves and rakes.
Felt – Fibrous material saturated with asphalt and used as an underlayment or sheathing paper.
Fiber Glass Mat – An asphalt roofing base material manufactured from glass fibers.
Flashing – Pieces of metal or roll roofing used to prevent seepage of water into a building around any intersection or projection in a roof such as vent pipes, chimneys, adjoining walls, dormers and valleys.
Flashing Cement – See Asphalt plastic cement.
G
Gable – The upper portion of a sidewall that corners to a triangular point at the ridge of a sloping roof.
Gable Roof – The upper portion of a sidewall that comes to a triangular point at the ridge of a sloping roof.
Galvanize – To plate with zinc, originally by shock galvanic action, providing protection from rust.
Granules – Ceramic, color-coated crushed rock that is applied to the exposed surface of asphalt roofing products.
Gutter – The trough that channels water from the eaves to the downspouts.
H
Hip – The inclined external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes. Runs from the ridge to the eaves.
Hip Roof – A type of roof containing sloping planes of the same pitch on each of four sides. Contains no gables.
L
Laminated Shingles – Strip shingles containing more than one layer of tabs to create extra thickness. Also called three-dimensional shingles.
Lead Pipe Jacks – A lead flashing installed over the PVC pipes that extend out through roof.
Low Slopes – Roof pitches less than a 4/12 pitch are considered low sloped roofs. Special installation practices must be used on roofs sloped 2/12-4/12.
M
Mansard Roof – A type of roof containing two sloping planes of different pitch on each of four sides. The lower plane has I much steeper pitch than the upper, often approaching vertical. Contains no gables.
Mastic – See asphalt plastic cement.
Membrane – A flexible or semi-flexible roof covering or waterproofing layer, whose primary function is the exclusion of water.
Modified Bitumen – Rolled roofing membrane with polymer modified asphalt and either polyester or fiberglass reinforcement.
N
Ninety-Pound (#90) – A prepared organic felt roll roofing with a granule surfaced exposure that has a mass of approx. 90 LBS per Square/100 Square feet.
NRCA – The National Roofing Contractors Association.
O
OpenValley – Method of valley construction is which shingles on both sides of the valley are trimmed along a chalk line snapped on each side of the valley. Shingles do not extend across the valley. Valley flashing is exposed.
OSB – Oriented Strand Board. A decking made from wood chips and lamination glues.
Overhang – That portion of the roof structure that extends beyond the exterior walls of a building.
P
Parapet Wall – The part of any wall entirely above the roof.
Pitch – The degree of roof incline expressed as the ration of the rise, in feet to the span, in feet.
Ply – The number of layers of roofing. Generally applied to flat roofs, i.e. one-ply, two ply.
Power Vents – Electrically powered fans used to move air from attics and structures. Installed through the decking.
R
Rafter – The supporting framing member immediately beneath the deck sloping from the ridge to the wall plate.
Rake – The inclined edge of a slope roof over a wall.
Ridge – The uppermost, horizontal external angle formed by the intersection of two sloping roof planes.
Ridge Shingles – Shingles used to cover the ridge. Also called ridge cap.
Rise – The vertical distance from the eaves line to the ridge.
Roll Roofing – Asphalt roofing products manufactured in roll form. Used on low to no sloped roofs.
S
Sheathing – Exterior grade plywood or tongue-and grove boards used as a roof deck.
Shed Roof – A roof containing only one sloping plane. Have no hips, ridges, valleys or gables.
Slope – The degree of roof incline expressed as the ration of the rise, in inches, in the run in feet.
Smooth-Surface Roofing – Roll roofing that is covered with ground talc or mica instead of granules.
Soffit – The finished underside of eaves.
Square – A unit of roof measure covering 100 square feet. A 10’ x 10’ section.
Starter Strip – Asphalt roofing applied at the eaves that provides protection by filling in the spaces under the cutouts and joints of the first course of shingles.
T
Three Tab Shingles – Flat asphalt roofing shingles. 20,25 & 30 year warranty. The cheapest form of shingles.
U
Underlayment – A layer of material under the roofing and on top of the decking. Mainly felt, #15 or #30.
V
Valley – The internal angle formed by the intersecting of two sloping roof planes.
Vent – Any outlet for air that protrudes through the roof deck such as a pipe of stack. Any device installed on the roof, gable or soffit for the purpose of ventilating the underside of the roof deck/attic.
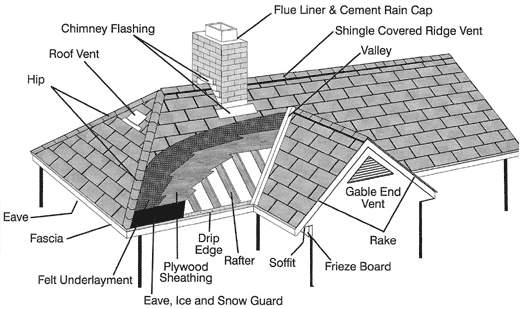
Roof Diagram
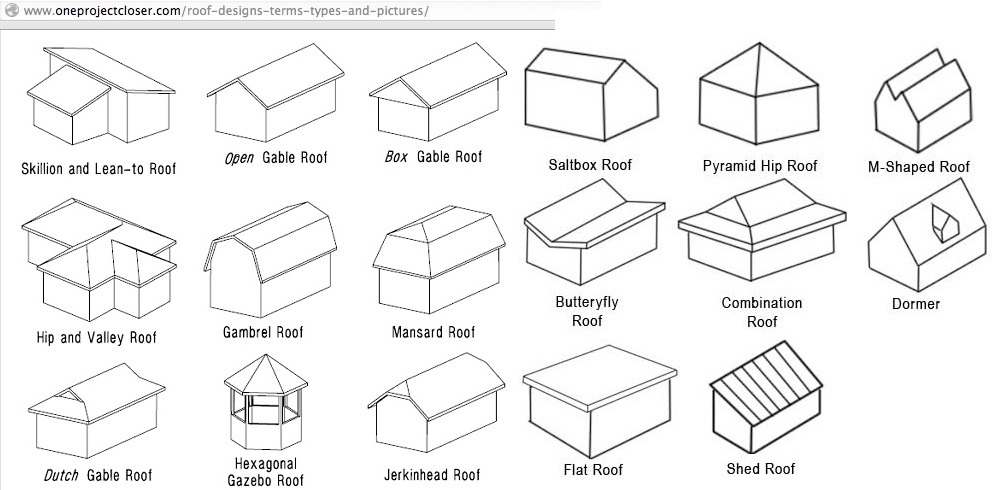
Roof Types
